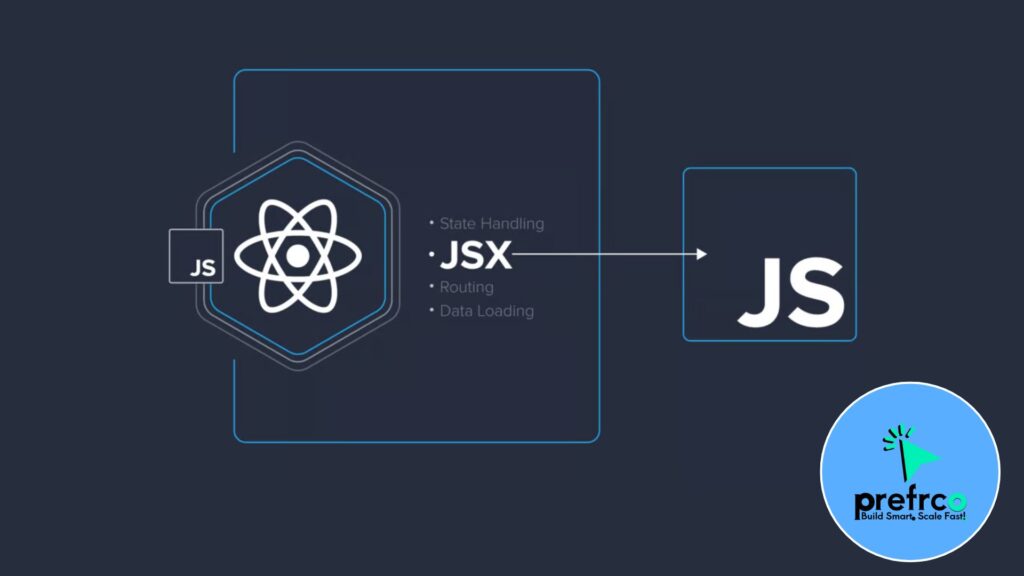
JSX stands for JavaScript XML and is a syntax extension for JavaScript, commonly used with React. It allows you to write HTML-like code within JavaScript, making it easier to create and manage UI components in React.
Here’s a basic example of JSX:

Key points about JSX:
- HTML-like syntax: It looks similar to HTML, but under the hood, JSX gets transpiled to
React.createElement()calls by tools like Babel. - Embedding Expressions: You can embed JavaScript expressions inside curly braces (
{}) within JSX.

Self-closing tags: In JSX, tags like <img /> or <input /> are self-closing, as opposed to HTML where you’d write <img></img>.
Class vs className: In JSX, class is written as className to avoid conflicts with the reserved JavaScript keyword.
Let’s dive deeper into JSX and its key concepts, features, and how it works within React.
1. JSX as a Syntax Extension
JSX is a syntax extension for JavaScript that allows you to write HTML-like code inside JavaScript. It’s mainly used with React to define what the UI should look like. When you use JSX, you can create React elements more intuitively, as if you are writing HTML directly in JavaScript.
However, JSX is not HTML—it is a syntactic sugar over JavaScript function calls. In the background, JSX is transformed into React.createElement() function calls, which ultimately generate React elements.
Example of JSX:
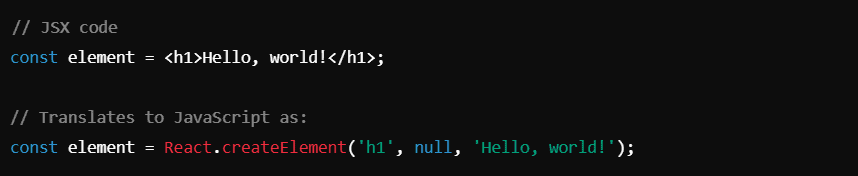
React uses this function to create virtual DOM elements. JSX simplifies the process of writing and visualizing UI components in JavaScript.
2. Embedding Expressions in JSX
You can embed any JavaScript expression inside curly braces {} within JSX. This includes variables, functions, or even mathematical operations.

In the above examples, {name} and {2 + 3} are JavaScript expressions embedded within the JSX.
3. JSX is Tightly Linked to React
When you write JSX, React takes care of converting the JSX into React.createElement() calls. This means React must be in scope for JSX to work correctly. Typically, you import React in your JavaScript files when you write JSX.
4. JSX and Rendering
React elements are plain JavaScript objects that describe what you want to appear on the screen. React uses the virtual DOM to optimize updates to the actual DOM, making the UI more efficient.
React elements can be rendered with the ReactDOM.render() method.

5. JSX as Expressions
JSX is an expression, which means it can be assigned to variables, passed as arguments, and returned from functions.

6. JSX Attributes
In JSX, HTML attributes are written in camelCase instead of lowercase. For example:
classbecomesclassNameforbecomeshtmlForstyleis written as an object with camelCase properties instead of a string.
Example:

In the style attribute, you need to pass an object with key-value pairs instead of a string.

7. Conditional Rendering in JSX
You can conditionally render JSX elements based on certain conditions using standard JavaScript logic, such as if, else, or ternary operators.
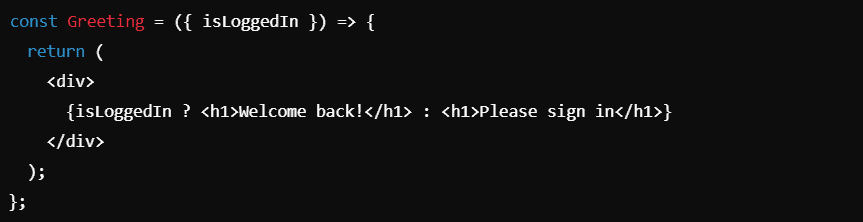
You can also use logical && operator for rendering elements conditionally:
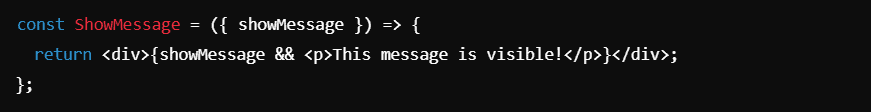
8. Lists and Keys in JSX
To render lists in React, you can use JavaScript’s map() function to iterate over an array and generate JSX elements. When rendering lists, keys are essential for efficient updates of the virtual DOM
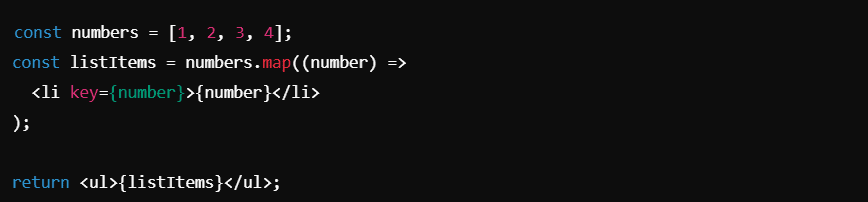
Here, the key prop helps React keep track of which items changed, added, or removed.
9. JSX Fragments
In some cases, you might want to return multiple elements from a component without adding extra nodes to the DOM. This is where fragments come in. Fragments allow you to group multiple elements without introducing a wrapper node.

You can also use React.Fragment:

10. JSX vs. HTML
- Self-closing tags: In HTML, tags like
<img>,<input>, and<br>don’t need a closing tag. In JSX, these tags must be self-closing:<img />,<input />,<br />. - Event handlers: In JSX, event handlers use camelCase. For example,
onclickin HTML becomesonClickin JSX. - Attributes: JSX uses
classNameinstead ofclassandhtmlForinstead offorto avoid conflicts with JavaScript keywords.
11. Transpiling JSX
Since browsers don’t understand JSX natively, tools like Babel transpile JSX code into regular JavaScript before it can run in the browser. JSX code is ultimately compiled down into React.createElement function calls.
For example, JSX:

Transpiles to:

12. Performance Considerations
Although JSX simplifies the development process, it doesn’t inherently impact performance. However, React’s virtual DOM ensures that only necessary updates are made to the actual DOM, which improves rendering performance.
Conclusion
JSX is a powerful and expressive tool that allows you to write React components in a way that closely resembles HTML. It makes the code more readable and declarative, especially for UI rendering. Understanding JSX is a fundamental step when learning React, and it’s essential for building modern web applications with this library.